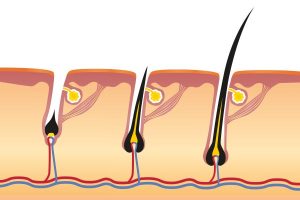
 Human hair growth is a dynamic process that is subject to certain growth cycles and repeats itself regularly.
Human hair growth is a dynamic process that is subject to certain growth cycles and repeats itself regularly.
A hair is not a lifelong companion: it only remains on your head for about two to six years. During this time, it goes through various phases:
1. Anagen phase (growth phase)
The growth or anagen phase lasts between two and six years. A hair grows about 1cm per month in this phase. On average, about 80 to 90% of all hair is currently in this phase.
2. Catagen phase (transitional phase)
After the hair growth period, the hair is separated from the hair root and gradually pushed in the direction of the scalp. This phase (also called catagen phase) lasts up to two weeks and concerns about 1% of all hair on the head.
3. Telogen phase (resting phase)
Now the hair is completely separated from the root and thus also from the nutrient supply. During this phase it can take three to four months for the hair to fall out.
Then, the hair follicle, which has pushed the old hair upwards to the scalp, moves back into the deeper layers of the skin. The metabolic process starts again from the beginning and the hair bulb produces cells again: a new hair grows. About 10 to 30% of the hair is currently in this stage.
Every day, a person loses 80 to 100 hairs due to the natural telogen phase, because not all hairs are in the same growth phase. Only if you count more than 100 hairs lost over a longer period of time could this be a sign of excessive hair loss.

